This FAQ is for Open MPI v4.x and earlier.
If you are looking for documentation for Open MPI v5.x and later, please visit docs.open-mpi.org.
Table of contents:
- What is netloc?
- What types of networks does netloc support?
- How do netloc and hwloc work together?
- What is "mapping"?
- What is a "reader"?
- How do I build netloc?
- What version of hwloc does netloc require?
- What is Jansson? Why does netloc require it?
- What if I have multiple networks?
- How do I discover the topology of an InfiniBand network?
- What OpenFlow Controllers are supported by netloc?
- How do I discover the topology of an Ethernet network using OpenFlow?
- How many API's are there? Which one(s) should I use?
- What is the Data Collection API?
- What is the Network Metadata API?
- What is the Network Topology Query API?
- What is the Map API?
- Are there any example programs that I can reference to get started?
- What are the netloc tools? How do I use them?
The Portable Network Locality (netloc) software package provides network
topology discovery tools, and an abstract representation of those networks
topologies for a range of network types and configurations. It is provided as a
companion to the Portable Hardware Locality (hwloc) package. These two software
packages work together to provide a comprehensive view of the HPC system
topology, spanning from the processor cores in one server to the cores in
another - including the complex network(s) in between.
Towards this end, netloc is divided into three components:
- Network topology discovery tools for each network type and discovery
technique (called readers).
- erging hwloc server topology information with that network topology
information to produce a unified map of an entire computing system (even if
that system includes multiple networks of different types, and servers that
are on at least one of those networks).
- A portable C API for higher-level software to query, traverse, and
manipulate the abstract representation of the network topology and unified map
(represented as a graph)
The network topology graph not only provides information about the physical
nodes and edges in the network topology, but also information about the paths
between nodes (both physical and logical, where available). Since the type of
analysis (e.g., graph partitioning) required of this graph is often
application-specific, netloc limits the amount of analysis it performs and
leaves further analysis to higher level applications and libraries built upon
this service. Additionally, the lsnettopo CLI tool can display and export this
network topology information in a variety of formats (e.g., GraphML and GEXF
file formats) providing developers with an additional mechanism to access the
data for further analysis.
Similar to hwloc, netloc primarily aims at helping applications with gathering
information about modern computing and networking hardware so as to exploit it
accordingly and efficiently.
| 2. What types of networks does netloc support? |
The project currently supports the following networks:
- Ethernet networks using OpenFlow
- InfiniBand networks
We are always working to support for additional networks. If there is a
particular network technology or configuration that you would like us to
support then please contact us on the development mailing list.
| 3. How do netloc and hwloc work together? |
The hwloc project provides a detailed view of the server topology from compute
cores to memory domains to PCI connected devices such as network cards. The
netloc core readers have the ability to discover the network topology from the
switches to each individual network card.
The netloc core readers themselves do not have enough information to determine
which network cards belong to the same server. By mapping the network topology
(discovered by the netloc core readers) with the hwloc server topology netloc
is able to group the network cards installed into the same server box. The
mapping joins these two topologies allowing the user to trace a path from a
processor core on one server to the cores in another through the network(s)
between them.
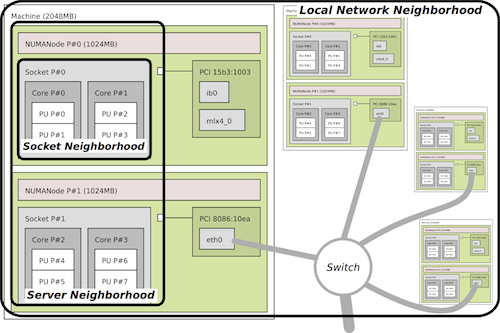
The netloc project uses the term "mapping" when we are combining the network
topology information with the server topology information. Specifically,
mapping joins together the network cards in the hwloc topologies to their
corresponding network interfaces in the netloc topology.
The mapping process also allows multiple types of and subnets within networks
to be accessed together. For example, if you have a cluster that has an
InfiniBand network and multiple Ethernet networks the mapping process will
connect these network topologies to the appropriate network cards in the server
topologies during the mapping phase. The end user can differentiate those two
networks by identifiers on their associated data structures.
A netloc "reader" is a command line tool that is used to access the network
topology for a specific network type. As such there is at least one reader for
each network type. The goal of the reader is to hide the discovery mechanism
from the end user, access the topology information, and preserve that network
topology information to a network independent format. The readers use the Data
Collection API internally to save the network topology information into a
netloc specific format.
| 6. How do I build netloc? |
The following only applies to netloc v0.5 since next releases will
be included in hwloc releases.
In general, all you need to do is expand the tarball, run the provided
configure script, and then run "make all install". For example:
1
2
3
4
5
| shell$ gunzip -c netloc-.tar.gz | tar xf -
shell$ cd netloc-
shell$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local
<...lots of output...>
shell$ make all install |
Note that the configure script supports a lot of different command
line options. For example, the --prefix option in the above example
tells netloc to install under the directory /usr/local/.
Consult the README
file in the netloc tarball and the output of "configure --help" for
specific instructions regarding netloc's configure command line options.
| 7. What version of hwloc does netloc require? |
The following only applies to netloc v0.5 since next releases will
be included in hwloc releases.
netloc requires a hwloc
version of 1.4.2 or later. There are some addtional features in hwloc 1.8 and
later that netloc can take advantage of as well (e.g., topology compression).
| 8. What is Jansson? Why does netloc require it? |
Jansson is C library for managing
JSON encoded data. Internally, netloc uses Jansson to store metadata and the
network topology.
netloc requires Jansson version 2.3 or later. The --with-jansson(=DIR)
configure option allows you to specifiy the location of the Jansson
library. The (=DIR) part means that specifying the directory is optional.
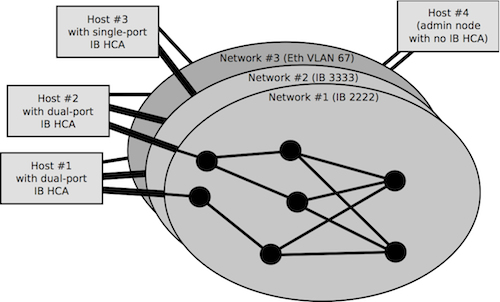
| 9. What if I have multiple networks? |
It not uncommon to have a cluster with multiple networks. Often an Ethernet
network and another high-speed interconnect, or multiple of the same type of
network. In these situations you will need to run the netloc reader for each of
the networks in your system. The readers will produce network files for each
network type. The mapping mechanism will allow the netloc project to join these
networks together at specific server end points for that comprehensive view of
the HPC system topology.
| 10. How do I discover the topology of an InfiniBand network? |
There are a few tools involved in discovering the topology of an InfiniBand
network. The following README provides more information about this
process:
README.infiniband
| 11. What OpenFlow Controllers are supported by netloc? |
We currently support the following OpenFlow controllers:
| 12. How do I discover the topology of an Ethernet network using OpenFlow? |
There are a few tools involved in discovering the topology of an Ethernet
network managed with an OpenFlow controller. The following README provides
more information about this process:
README.openflow
| 13. How many API's are there? Which one(s) should I use? |
The netloc project has four sections to its API, each listed below.
- Data Collection API
- Network Metadata API
- Network Topology Query
- Map API
If you are an application programmer you will probably want to focus on APIs
#2, #3, and #4. If you are interested in developing a reader for a new network
then you will want to look at API #1.
| 14. What is the Data Collection API? |
This API is used by the readers to create the netloc-common .ndat topology
files. This API can be used by other system services (e.g., resource managers,
MPI) to produce .ndat files that represent a subset of the network, or to
further annotate the network information.
Futher details can be found in the header linked below:
/include/netloc_dc.h
| 15. What is the Network Metadata API? |
This API is used by the application to access high level information about the
network types and subnets available on the system without pulling all of the
network information. An application may use this API to search for a specific
type of network or subnet, or to request information about all available
networks.
Futher details can be found in the header linked below:
/include/netloc.h
| 16. What is the Network Topology Query API? |
This API is used by the application to access specific information about nodes
and edges in a single network subnet graph.
Futher details can be found in the header linked below:
/include/netloc.h
Futher details can be found in the header linked below:
/include/netloc_map.h
| 18. Are there any example programs that I can reference to get started? |
The netloc repository contains a few examples in the tests sub-directory:
/tests
A few exemplars to get you started:
- The map_paths.c
test provides the path between two processors on separate servers.
- The test_metadata.c
demonstrates ways to use the Network Metadata API to discover sets of networks.
| 19. What are the netloc tools? How do I use them? |
The netloc project creates a small collection of tools to help users collect
and analyze the network topology. Each tool is listed below with a link to
further documentation about how to use it properly.
- Network Readers
- lsnettopo
A tool to display a textual representation of the network topology. It can also export the graph to some standard graph file formats.
- netloc_ib_extract_dats
A tool to assist in the extraction of netloc data from raw InfiniBand data. (see this FAQ for more details).
- netloc_ib_gather_raw
A tool to assist in the gathering of raw InfiniBand data. (see this FAQ for more details).
|